Island Models using MPI
This is a somewhat advanced topic. If you are new to parallel computing, we recommend reading the page on Parallelism first.
EvoLP has newly implemented support for island models of evolutionary algorithms as an extension. The extension, EvoLPIslands, is implemented using the weak dependency feature added to Julia in v1.9.
Loading the extension
EvoLPIslands will be activated if and only if you have both EvoLP and MPI loaded into your current scope via the using or import keywords.
About Island Models
In an island model, multiple populations (or islands) evolve concurrently, and a subpopulation (or deme) occasionally drifts from one island to another in a process called migration. Migration passively helps with diversity preservation, which in turn benefits the exploration of large search spaces.
Migration
The migration process is broken down in three steps: drift, strand and reinsert!:
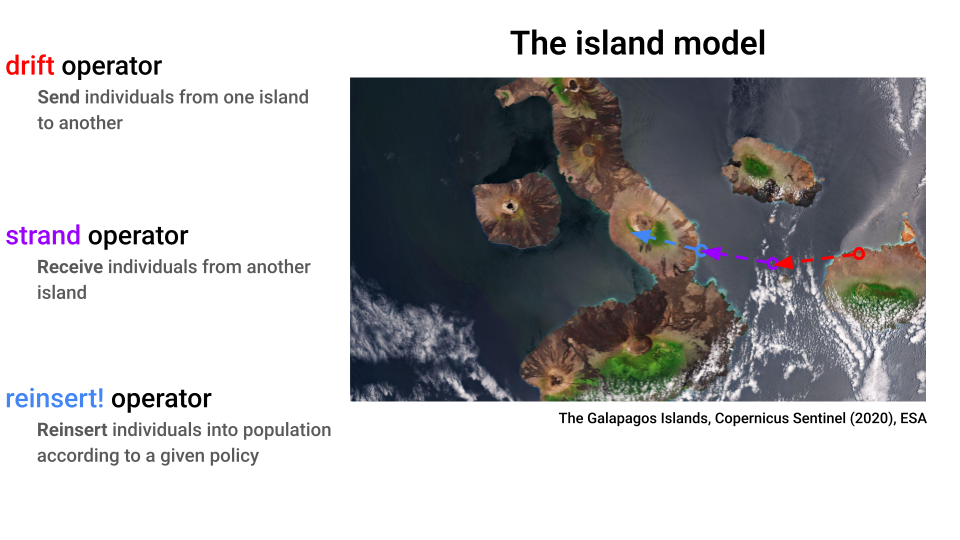
To implement these operators, EvoLP uses MPI.jl, a wrapper of MPI for Julia. MPI is a communication standard available in many parallel computing architectures, most notably High Performance Computing clusters, but it can also be used in your local machine.
Specifically, EvoLP uses the Send and Receive MPI directives, which are blocking. However, there is no need to use these directly. Instead, using the drift, strand, and reinsert! operators in your algorithms should suffice.
EvoLP.drift — Functiondrift(S_M::DemeSelector, population, y, dest; comm=MPI.COMM_WORLD)Select and send individuals from population to the dest island, according to the deme selector S_M and considering their fitnesses y.
Returns a 2-tuple containing the sent deme, and its MPI_Request.
EvoLP.strand — Functionstrand(S_M::DemeSelector, d, src; comm=MPI.COMM_WORLD)Receive d-dimensional individuals from src. The deme selector S_M is used to decode the received information.
Returns a 2-tuple containing the received deme, and its MPI_Request.
EvoLP.reinsert! — Functionreinsert!(population, y, R_M::DemeSelector, M)(Re)insert a deme M into the population, according to reinsertion criterion provided by the R_M deme selector, and the population's fitnesses y.
The new individuals will be appended into population.
Returns the indices of the deme that must be deleted.
Selecting a Deme
To send, receive, and reinsert a deme, we introduced DemeSelectors that allow for two different types of selection: random, and worst.
EvoLP.RandomDemeSelector — TypeDeme selector for obtaining a random sample of size k
EvoLP.WorstDemeSelector — TypeDeme selector for obtaining the worst k individuals
As with other operators in EvoLP, the deme selectors can be passed to the select method—both for selecting the deme that will migrate as well as selecting the deme that will be replaced.
EvoLP.select — Methodselect(S_M::RandomDemeSelector, y)Return a list of size S_M.k of random indices from a vector of fitnesses y. Used inside drift to select individuals to be sent to another island, or inside reinsert! to select individuals to be replaced.
EvoLP.select — Methodselect(S_M::WorstDemeSelector, y)Return the indices of the S_M.k-worst fitnesses in y. Used inside drift to select individuals to be sent to another island, or inside reinsert! to select individuals to be replaced.
We also provide a built-in toy algorithm, the island GA:
EvoLP.islandGA! — Functionfunction islandGA!(
logbook::Logbook,
f::Function,
population::AbstractVector,
max_it::Integer,
S_P::EvoLP.Selector,
X::EvoLP.Recombinator,
Mut::EvoLP.Mutator,
μ::Integer,
S_M::DemeSelector,
R_M::DemeSelector,
dest::Integer,
src::Integer,
comm::MPI.COMM_WORLD)Generational genetic algorithm with islands.
Arguments
logbook::Logbook: to save Statisticsf::Function: objective function to minimisepopulation::AbstractVector: a list of vector individualsmax_it::Integer: number of iterationsS_P::ParentSelector: one of the availableEvoLP.SelectorX::Recombinator: one of the availableEvoLP.RecombinatorMut::Mutator: one of the availableEvoLP.Mutatorμ::Integer: migration rate (in number of iterations)S_M::DemeSelector: selection policy. One of the availableEvoLP.DemeSelectorR_M::DemeSelector: replacement policy. One of the availableEvoLP.DemeSelectordest::Integer: ID of destination islandsrc::Integer: ID of source islandcomm::MPI.Comm: an MPI communicator. UsuallyMPI.COMM_WORLD.
Further Reading
- Our paper Evolutionary Computation with Islands: Extending EvoLP.jl for Parallel Computing.
- EvoLP's Parallel documentation page.
- The MPI.jl documentation.